

Next: The Heuristics
Up: THE REASONING STRATEGY
Previous: Appropriateness
The following axioms allow us to define
precisely the space of mental situations.
We use variables for
blocks (x, y, z, w, ...), for
situations (s,  , ...), for
actions (a,
, ...), for
actions (a,  , ...), for mental
situations (m,
, ...), for mental
situations (m,  , ...), for
mental actions (
, ...), for
mental actions (  ,
,  ,
...), for formulas in the database (f,
,
...), for formulas in the database (f,
 , ...), for subgoals -formulas
in the goal stack- (g,
, ...), for subgoals -formulas
in the goal stack- (g,
 , ...), for sequences of actions,
(r,
, ...), for sequences of actions,
(r,  , ...), and for sequences of
mental actions (l,
, ...), and for sequences of
mental actions (l,  , ...).
, ...).
We assume uniqueness of names for
every function symbol h, and every pair
of distinct function symbols h and g.
The symbols h and g are syntactical
variables ranging over distinct function
symbols; the symbols  to
to  are
syntactical variables ranging over block
constants. Axiom
are
syntactical variables ranging over block
constants. Axiom 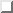 defines the expression
defines the expression  [12], which means that
mental situation
[12], which means that
mental situation  can be
reached from mental situation
m by executing a nonempty sequence
of appropriate mental actions
(
can be
reached from mental situation
m by executing a nonempty sequence
of appropriate mental actions
(  is an abbreviation for
is an abbreviation for
 ). We include
domain closure axioms for blocks,
mental situations, actions, and mental
actions. Axiom
). We include
domain closure axioms for blocks,
mental situations, actions, and mental
actions. Axiom 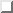 of
induction allows us to prove that a
property holds for all mental
situations that are reachable from
a given mental situation.
of
induction allows us to prove that a
property holds for all mental
situations that are reachable from
a given mental situation.

Josefina Sierra
Tue Jul 21 09:26:01 PDT 1998
 , ...), for
actions (a,
, ...), for
actions (a,  , ...), for mental
situations (m,
, ...), for mental
situations (m,  , ...), for
mental actions (
, ...), for
mental actions (  ,
,  ,
...), for formulas in the database (f,
,
...), for formulas in the database (f,
 , ...), for subgoals -formulas
in the goal stack- (g,
, ...), for subgoals -formulas
in the goal stack- (g,
 , ...), for sequences of actions,
(r,
, ...), for sequences of actions,
(r,  , ...), and for sequences of
mental actions (l,
, ...), and for sequences of
mental actions (l,  , ...).
, ...).
 to
to  are
syntactical variables ranging over block
constants. Axiom
are
syntactical variables ranging over block
constants. Axiom  [
[ is an abbreviation for
is an abbreviation for
 ). We include
domain closure axioms for blocks,
mental situations, actions, and mental
actions. Axiom
). We include
domain closure axioms for blocks,
mental situations, actions, and mental
actions. Axiom 